DataOps, a set of practices that combine software engineering principles with data management, can significantly enhance data privacy and compliance. By automating data pipelines, improving collaboration, and reducing time to market, DataOps empowers organizations to protect sensitive data and adhere to regulatory requirements.
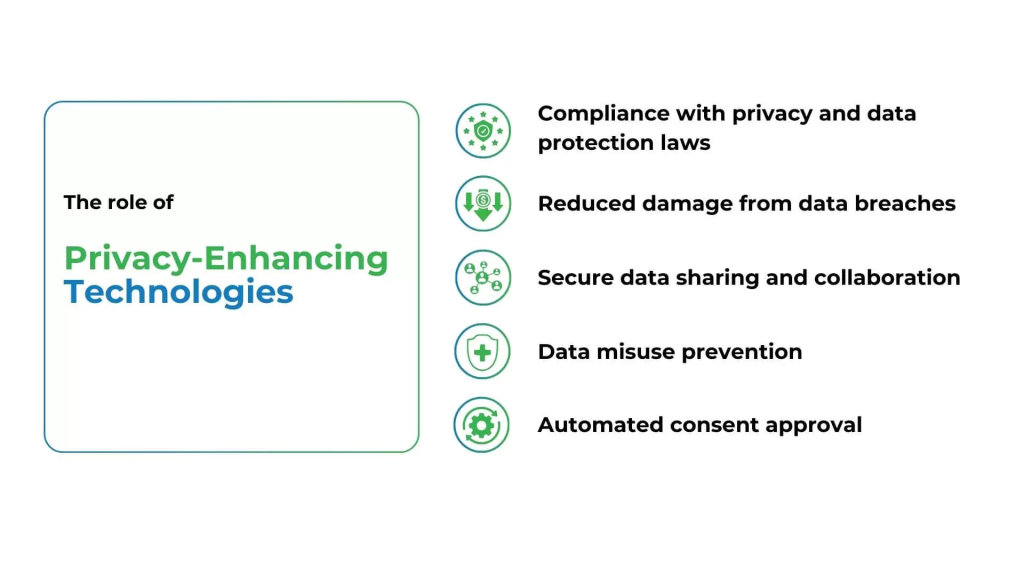
How DataOps Enhances Data Privacy and Compliance
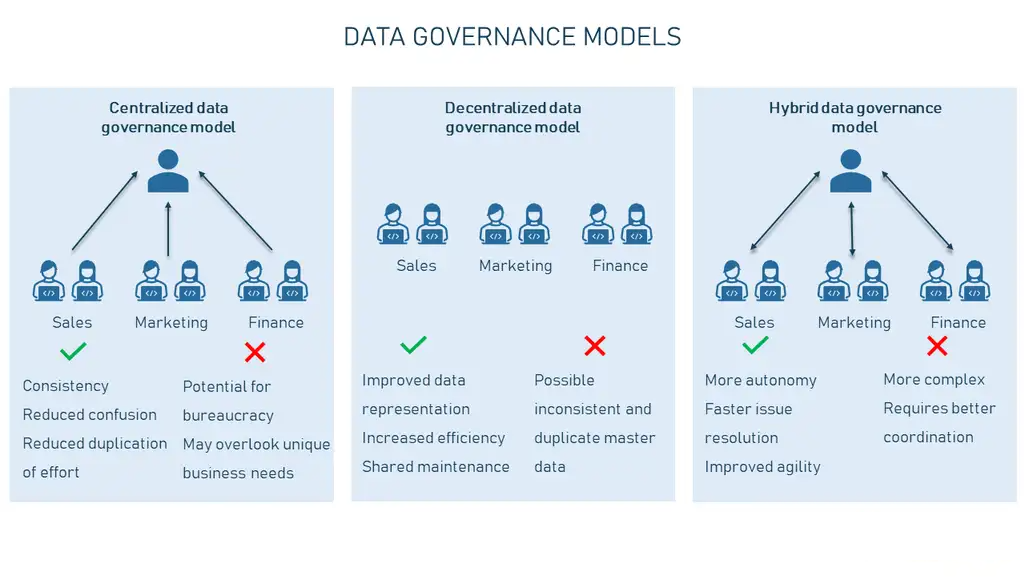
- Centralized Data Governance:
- Clear Ownership and Accountability: Defines clear data ownership and accountability.
- Enforced Data Access Controls: Restricts access to sensitive data based on roles and permissions.
- Adherence to Data Privacy Regulations: Ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
- Automated Data Pipelines:
- Reduced Human Error: Minimizes the risk of human error by automating data pipelines.
- Data Quality Checks: Implements automated checks to identify and correct data quality issues.
- Secure Data Transfers: Uses secure protocols and encryption to protect data during transmission.
- Robust Monitoring and Alerting:
- Monitors Data Access: Tracks user access to sensitive data.
- Detects Anomalies: Sets up alerts for unusual data patterns or security breaches.
- Implements Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitors network traffic for malicious activity.
- Data Encryption:
- Protects Sensitive Data: Encrypts data at rest and in transit.
- Uses Strong Encryption Algorithms: Implements robust encryption algorithms like AES-256.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing:
- Identifies Vulnerabilities: Conducts regular security audits to identify weaknesses.
- Simulates Attacks: Performs penetration testing to assess the organization’s security posture.
- Patch Management: Keeps systems and software up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Data Masking and Anonymization:
- Protects Sensitive Data: Masks or anonymizes sensitive data to reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Complies with Privacy Regulations: Ensures compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Incident Response Planning:
- Develops an Incident Response Plan: Creates a detailed plan for responding to security incidents.
- Tests the Plan Regularly: Conducts regular drills to ensure the plan is effective.
- Establishes a Crisis Communication Plan: Communicates effectively with stakeholders during security incidents.
- Employee Training and Awareness:
- Security Awareness Training: Educates employees about security best practices.
- Phishing Awareness: Trains employees to recognize and avoid phishing attacks.
- Password Security: Implements strong password policies and encourages the use of multi-factor authentication.