Linux is a powerful and versatile operating system, widely used for its robustness and flexibility. Understanding basic Linux commands is essential for efficiently managing and navigating a Linux system. In this tutorial, we’ll cover some fundamental Linux commands along with practical examples.
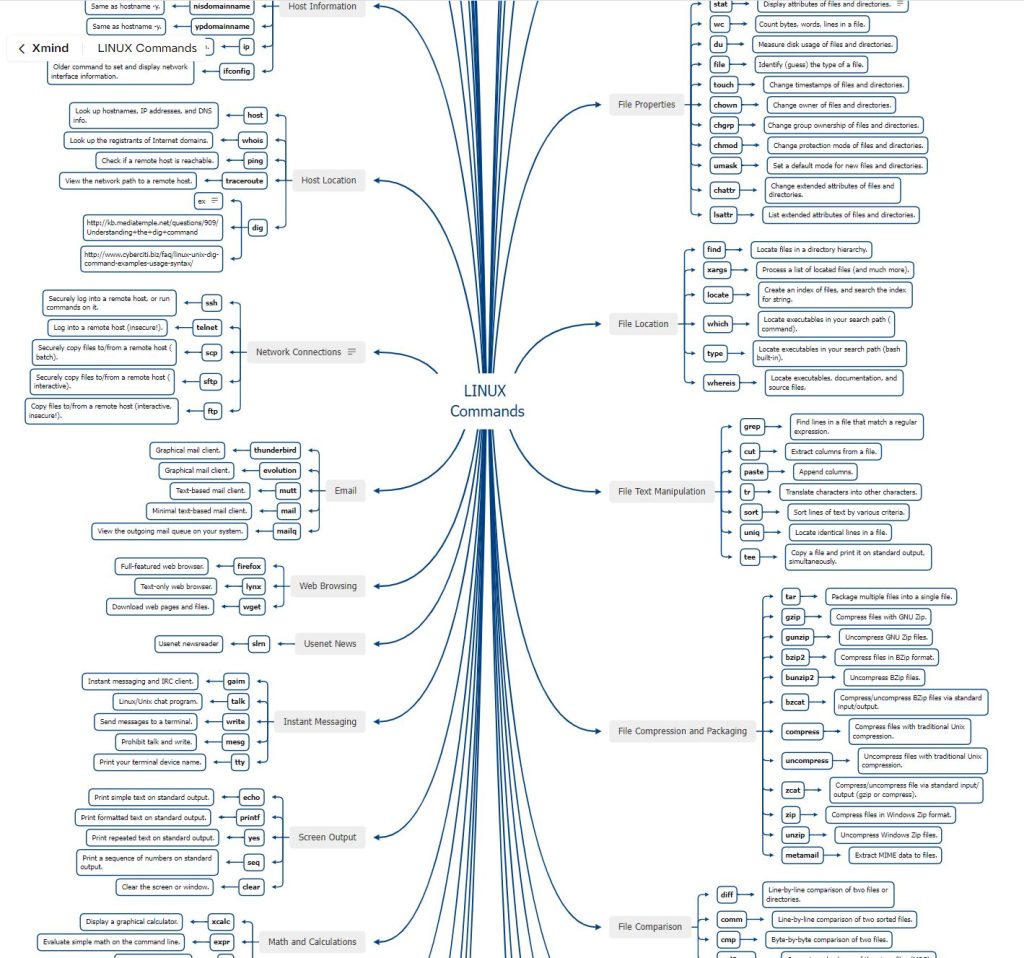
Table of Contents
- Navigating the File System
- File and Directory Management
1. Navigating the File System
ls – List Directory Contents
The ls command lists the contents of a directory.
lsExample:
ls -lThis lists files in long format, showing detailed information.
cd – Change Directory
The cd command changes the current working directory.
cd /path/to/directoryExample:
cd /home/user/DocumentsThis changes the current directory to /home/user/Documents.
pwd – Print Working Directory
The pwd command displays the current working directory.
pwdIf you are in /home/user, it will output /home/user.
2. File and Directory Management
mkdir – Make Directory
The mkdir command creates a new directory.
mkdir directory_nameExample:
mkdir roshanThis creates a directory named roshan.
rm – Remove Files or Directories
The rm command removes files or directories.
rm file_nameExample:
rm -r directory_nameThis removes a directory and its contents recursively.
Hopefully, It will help you ..!!!