
Looping in programming languages is a feature which facilitates the execution of a set of instructions/functions repeatedly while some condition evaluates to true. For example, suppose we want to print “Manish Kumar” 5 times. This can be done with ease with the help of loop:
In Loop, the statement needs to be written only once and the loop will be executed 10 times as shown below:
You can observe that in the above program using loops we have used the document.write statement only once but still, the output of the program will be same as that of the iterative program where we have used the document.write statement 5 times.
There are mainly two types of loops:
Entry Controlled loops: In this type of loops the test condition is tested before entering the loop body. For Loop and While Loop are entry controlled loops.
Exit Controlled Loops: In this type of loops the test condition is tested or evaluated at the end of loop body. Therefore, the loop body will execute at least once, irrespective of whether the test condition is true or false. Do – while loop is exit controlled loop.
JavaScript mainly provides three ways for executing the loops. Let us learn about each one of these in details.
While loop: A while loop is a control flow statement that allows code to be executed repeatedly based on a given Boolean condition. The while loop can be thought of as a repeating if statement.
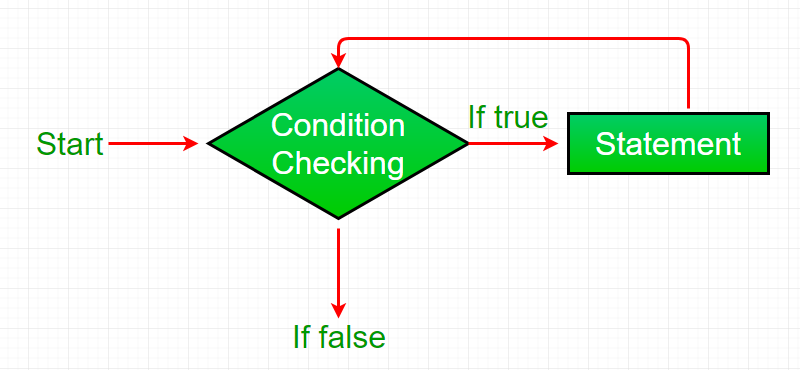
- While loop starts with the checking of condition. If it evaluated to true, then the loop body statements are executed otherwise first statement following the loop is executed. For this reason it is also called Entry control loop
- Once the condition is evaluated to true, the statements in the loop body are executed. Normally the statements contain an update value for the variable being processed for the next iteration.
- When the condition becomes false, the loop terminates which marks the end of its life cycle.
For loop: for loop provides a concise way of writing the loop structure. Unlike a while loop, For statement consumes the initialization, condition and increment/decrement in one line thereby providing a shorter, easy to debug structure of looping.

- Initialization condition: Here, we initialize the variable in use. It marks the start of a for loop. An already declared variable can be used or a variable can be declared, local to loop only.
- Testing Condition: It is used for testing the exit condition for a loop. It must return a Boolean value. It is also an Entry Control Loop as the condition is checked prior to the execution of the loop statements.
- Statement execution: Once the condition is evaluated to true, the statements in the loop body are executed.
- Increment/ Decrement: It is used for updating the variable for next iteration.
- Loop termination: When the condition becomes false, the loop terminates marking the end of its life cycle.
Do while: do while loop is similar to while loop with only difference that it checks for condition after executing the statements, and therefore is an example of Exit Control Loop.
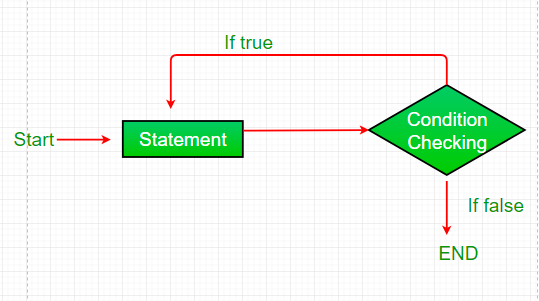
- Do while loop starts with the execution of the statement(s). There is no checking of any condition for the first time.
- After the execution of the statements, and update of the variable value, the condition is checked for true or false value. If it is evaluated to true, next iteration of loop starts.
- When the condition becomes false, the loop terminates which marks the end of its life cycle.
- It is important to note that the do-while loop will execute its statements at least once before any condition is checked, and therefore is an example of exit control loop.
In the above example, code will execute for the First time and increment and at last it will go and check the provided condition, and here the condition is False. so code will not execute further.
The bottom line is , either the condition is False in Do While Loop the code will must execute for the one time.
This is mainy used in testing of codes for its proper functioning.
I hope you like this particular information about LOOPs in JavaScript helpful and informative.
Thank You!!